
What Are Synthetic Derivatives?
Synthetic derivatives in DeFi are programmable financial contracts that replicate the payoff of traditional futures or options – without relying on centralized intermediaries. These instruments allow users to gain long or short exposure to crypto assets using smart contracts and oracles, giving full transparency and control.
Top Protocols Powering Synths:
-
Synthetix: Pioneer in minting on-chain synthetic assets (synths)
-
Polynomial: Automates options vault strategies
-
Derive (formerly Lyra): Focuses on AMM-based options with Greek risk modeling
Constructing Long/Short Positions Without Custody
Synthetic positions are typically built by collateralizing a base token (like ETH or USDC) and minting a synthetic asset that tracks the price of a target asset (e.g., sBTC or sETH).
📉 Short Position:
-
Mint a synthetic asset (sBTC)
-
Swap for stablecoin (sUSD)
-
Benefit if BTC drops
📈 Long Position:
-
Simply hold the synth (sBTC)
-
Increase in value as BTC rises
✅ No need to borrow or lend ✅ No reliance on centralized order books ✅ Positions are verifiable on-chain
📈 Decentralized Perpetual Platforms
Some DeFi platforms take synthetic trading further by enabling leverage, margin, and perpetual contracts:
-
gTrade (Gains Network): Synthetic leverage up to 150x
-
GMX: Utilizes price feeds and liquidity pools for leveraged perp trading
How Pricing Oracles and Liquidity Work in Synth Markets
Synthetic markets rely heavily on oracle accuracy. Mispricing can lead to loss or exploitation.
🔗 Chainlink, Pyth, and UMA are commonly used oracles. Key metrics:
-
Speed of updates
-
Decentralization of data feeds
-
Economic incentives for correctness
Liquidity typically comes from AMMs or protocol-owned liquidity. On Lyra, for instance, options are priced by an AMM with volatility and skew baked into pricing.
Risks of Synthetic Derivatives
Smart Contract Risk: Bugs or exploits in the protocol
Oracle Risk: Inaccurate or delayed price feeds
Counterparty Risk (minimal): Smart contracts remove human intermediaries, but systemic risk still exists if protocol incentives aren’t aligned
Slippage & Front-running: AMM-based platforms can be vulnerable to MEV attacks
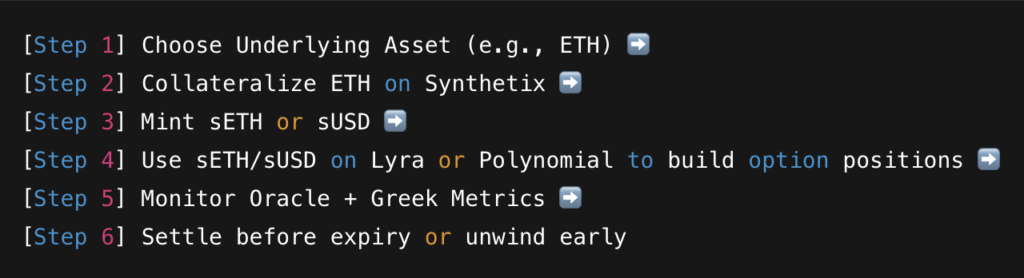
Building Synthetic Options
Here’s how to construct a synthetic option using DeFi tools:
Why Go Synthetic?
-
No KYC or CEX account needed
-
Global, unstoppable access
-
Programmable logic (auto roll, expiry logic, Greek strategies)
-
Trade volatility, interest rates, or composite indices






