
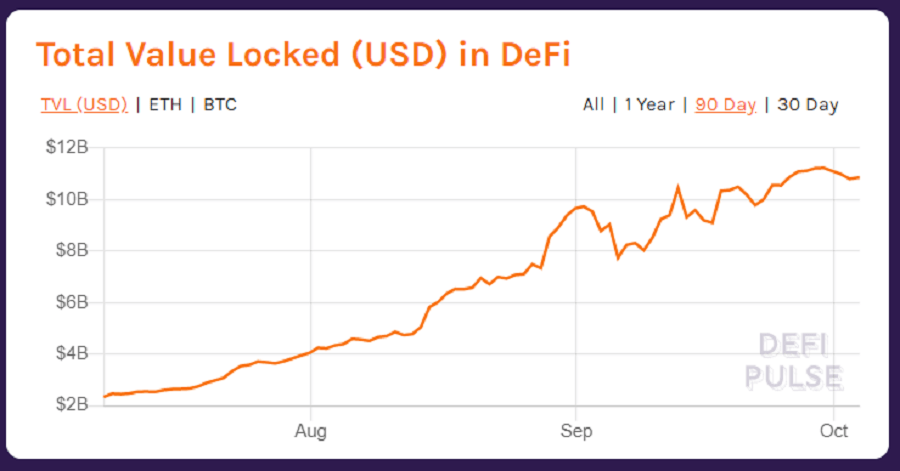
DeFi is a new financial sector. It has been around for about two years but has only recently begun to see significant growth. Over the last year alone, the total value “locked” in DeFi exceeded 10 billion USD and continues to rise. Users are rushing into the space for many reasons, but primarily due to the high interest rates offered by DeFi applications, which have exceeded 2000% in some cases.
This activity has drawn the attention of famous tech giants such as IBM which are now trying to bridge the gap between traditional finance and DeFi. Some DeFi applications have even become licensed and regulated, begging the question of how long it will be before DeFi applications are being used by the average person.
By the end of this article, you will have a firm grasp of what DeFi is, how it works, if DeFi is safe, and a few details about some of the most popular DeFi applications.
What is DeFi?
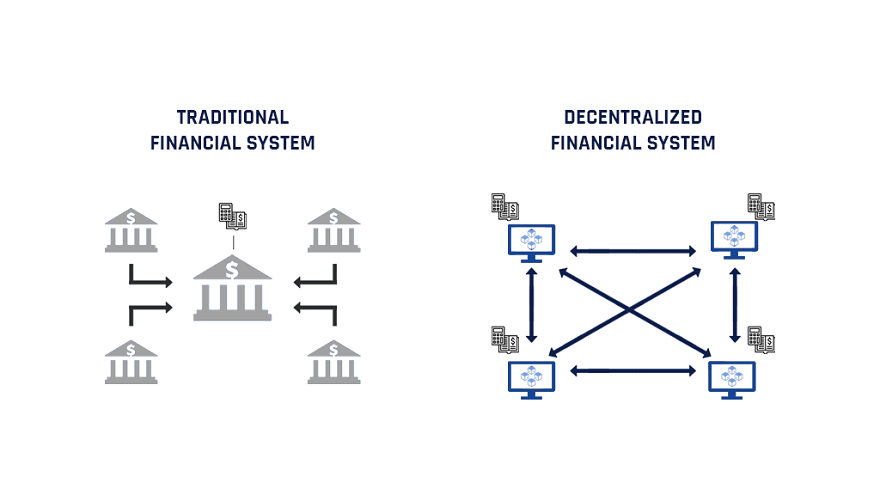
DeFi is short for decentralized finance. The DeFi space is made up of dozens of applications which provide traditional financial services such as lending, borrowing, saving, and insurance. The primary difference between DeFi and centralized finance is that these services are not provided by a central authority such as a bank or insurance company. Instead, they are powered by a series of automated programs called smart contracts.
How does DeFi work?
Most applications in DeFi are built using Ethereum, the second largest cryptocurrency after Bitcoin by market capitalization. The Ethereum blockchain, which records cryptocurrency transactions, also doubles as a platform which allows for the creation of the aforementioned automated smart contracts. As mentioned earlier, DeFi applications fundamentally consist of multiple smart contracts working together.
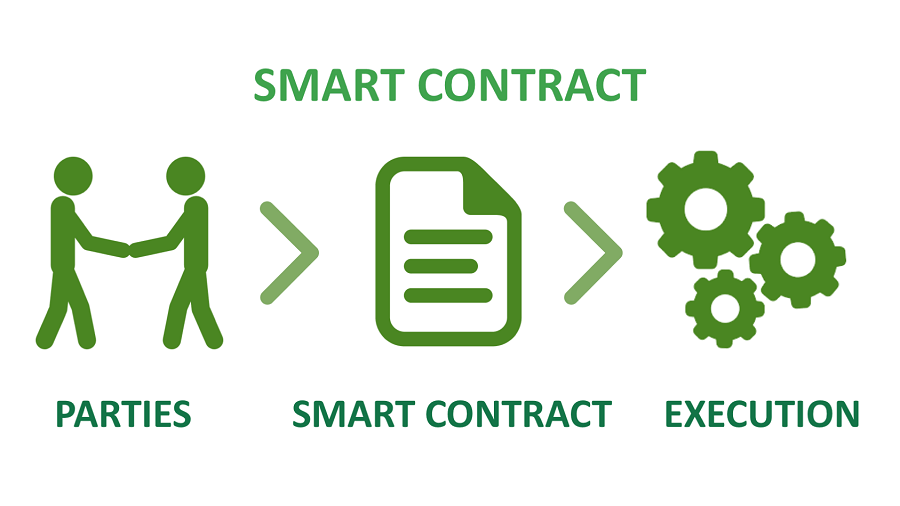
Smart contracts on Ethereum are built in much the same way that a regular computer program is built. They are built using a coding language called Solidity which is similar to the popular Javascript programming language. The primary difference between smart contracts and regular computer programs is that in most cases, smart contract applications cannot be modified once they have been launched.
Is DeFi safe?
This depends on who you ask. Those unfamiliar with cryptocurrency may feel uncomfortable putting their money into an automated program. On the other hand, many cryptocurrency supporters believe DeFi applications will eventually be more secure than centralized alternatives. There are four main reasons for this.
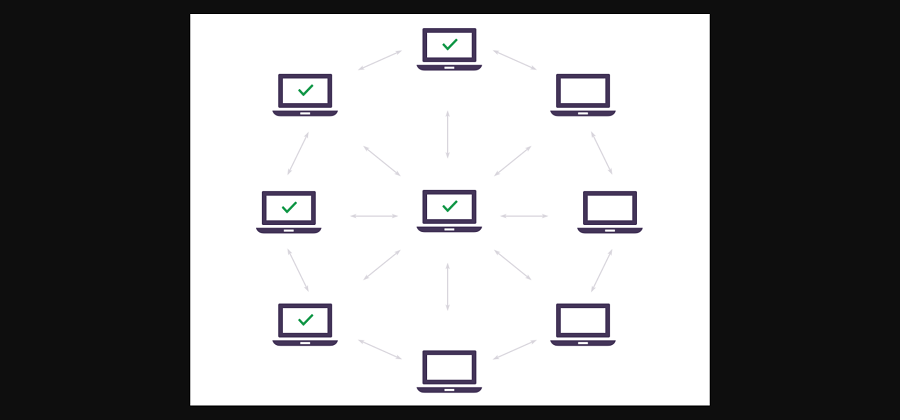
First, because DeFi applications are built on the Ethereum blockchain, there is little risk that they would ever experience an outage. This is because blockchains store transaction data, including the smart contracts which run these DeFi applications, across multiple (literally millions) of computers around the world.
Almost everyone has experienced a website or application that was unavailable due to an outage. This is because the overwhelming majority of websites and applications are stored in centralized servers. If something goes wrong with these servers (such as a power outage), users are unable to access that website or application. This is essentially impossible for DeFi applications for the reason in the previous paragraph.

Second, most smart contracts which make DeFi applications cannot be modified once they have been launched. This means that nobody is able to hack or corrupt the application. However, this assumes that the smart contracts were built correctly. There have been a handful of cases where poorly made smart contracts resulted in the loss of user funds. Thankfully, audits (reviews) of the Solidity code used to build them are becoming the new standard in DeFi.
Third, all transactions made in DeFi applications are publicly viewable and verifiable, and in many cases the code used to build the smart applications which power them is also open source (available for anyone to see). This means that users of the platform (and someday regulators) can know exactly where funds are at all times. Funds deposited into DeFi applications can also often be withdrawn at any time with little to no penalties.

Compare these last three points to legacy financial institutions which, being centralized and run by humans, are therefore more prone to corruption. A few individuals can get together and conspire to change the rules to their benefit, to modify records, and/or to steal funds. This has happened before and it will continue to happen no matter how many barriers are put in place to prevent these events from occurring. And of course, there are lots of fees, penalties, and complicated conditions for the financial services these centralized entities provide.
What are some examples of DeFi applications?

While there are hundreds of DeFi applications, only about 50 of them hold any substantial value in them, and the top 10 hold over 90% of the USD value “locked” in DeFi. DeFi applications can be broken down into following categories: lending protocols, decentralized exchanges, insurance, and aggregators.
DeFi Lending Protocols
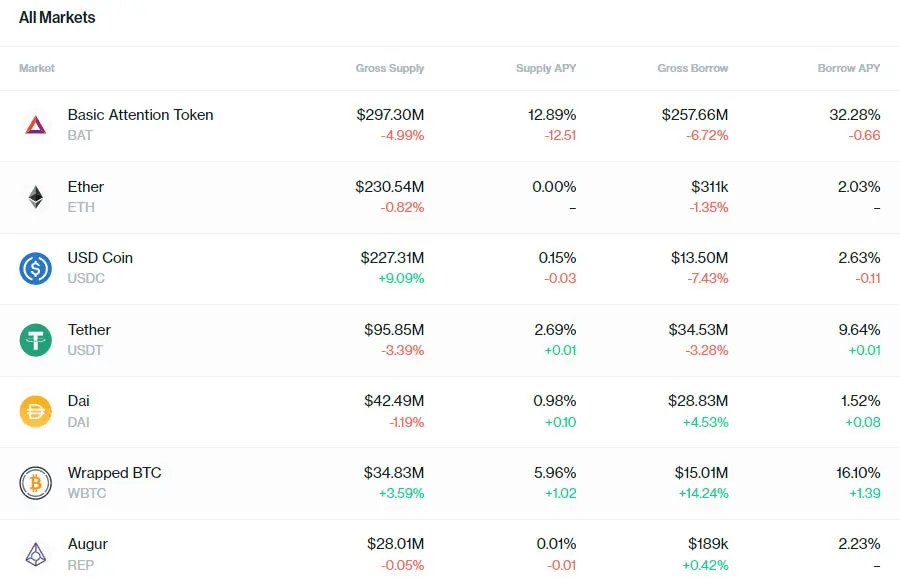
Examples of DeFi lending protocols include Compound and Aave. These applications let you lend and borrow cryptocurrencies with no credit checks or identification. The catch is that your collateral (how much you deposit to borrow) always has to be worth more in USD than what you are borrowing. This seems pointless but can be very useful if you want to borrow money without having to sell your cryptocurrency.
There is no deadline to pay back the loan and the interest rate varies depending on the supply and demand for the asset you are lending or borrowing. Lenders can earn anywhere from 0.1%-20%+ interest per year on the funds they deposit onto these platforms for other users to borrow and higher interest rates apply for borrowed assets. Lenders can withdraw their assets from these lending protocols at any time with no penalty.
Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges (also known as DEXs), allow users to trade cryptocurrency in a decentralized manner. This means that the exchange will never go down (since there is no central point of failure) and assets are also able to remain on users’ own wallets and do not need to be transferred to a centralized wallet which could be vulnerable to hacks. Uniswap and Kyber Network are two popular decentralized exchanges.
DEXs incentivize users to use their platforms by rewarding them for providing liquidity to the exchange. This is a fancy term for “locking” money into the decentralized exchange so that traders who are using the platform are not left waiting for their trade to complete. The rewards for providing liquidity come from giving liquidity providers a small cut of the trading fees on these exchanges (e.g. 0.1% of every trade). Funds can also be withdrawn at any time with no penalty.
DeFi Insurance

If you are risk averse but still want to use these DeFi protocols, you can get decentralized insurance from DeFi projects such as Nexus Mutual and Etherisc. The former lets you insure funds you deposit on other DeFi protocols such as Compound and Aave. The latter lets you create your own insurance products and plans to cover things such as delayed flights! Although these platforms are created by centralized parties, all funds are controlled by the users of the platform.
DeFi Aggregators
Aggregators are DeFi applications which automatically transfer your funds between other DeFi applications. This is done to either maximize the interest you are receiving on deposited funds or to let you trade more efficiently. For example, yearn.finance aggregates multiple lending protocols and automatically moves your funds to the one which will give you the highest interest on your assets.

Similarly, 1nch, a DEX aggregator, taps into multiple DEXs to make your trades faster and in some cases even get you a better price. Aggregators use liquidity mining schemes similar to DEXs, providing rewards to users who deposit funds onto their platforms to make them even better for people who are actively using them. In contrast to DEXs, this is often done by issuing governance tokens, tradeable cryptocurrencies which let you vote on how to change the aggregator.
With all this said, we have only just scratched the surface of this incredible new financial sector. There are new developments in DeFi almost every day, and some of the technologies being invented “DeFi” the laws of finance. Flash loans, elastic currencies, and synthetic assets are unfortunately outside the scope of this article, but will be front and center in more to come. Spread the word and stay tuned, because there is a lot more cover that you need to know!






